Overview
Table of Contents
Overview
So, hello guys, welcome back to the gettobyte YouTube channel. The video you have just seen is the encryption-decryption of an image using Microcontrollers. And that’s what we will implement and learn to do in today’s video.

We are going to explore, how to use cryptography technology in microcontrollers. Will be doing the hands-on activity for encryption/decryption of data and images using the ElecronicsV2 Development board. Encryption/Decryption is the cryptography concept and what we are going to achieve on doing so is to know how to use cryptography technology through microcontrollers.
For doing Encryption/decryption we are using the AES cryptography algorithm, which is supported in the ElecronicsV2 development board through its SHE standard-based CSEc peripheral. For those who are new to the channel and world of cryptography technology, would recommend watching these videos in the following hierarchical order to get an understanding of cryptography and the technical terms that have been stated just now.
What is Cryptography
How Cryptography is implemented in Microcontrollers
DIY Project Statement
What i have done here is take an image, which is an original image and convert it into a string of bytes. After that, wrote software to store that string of bytes in the ElecronicsV2 development board and to do encryption through AES cryptography algorithm on the stored data. On successful encryption, those string of bytes are changed to the encrypted format of data and then that encrypted data is processed to print the encrypted image on color LCD Screen. This is just a basic demo on how to use cryptography technology for securing the original data. Here we are printing encrypted image on the LCD Screen, Same way we can send, encrypted image data to other microcontroller via CAN, LIN or any other protocol. Will be doing this activity too in upcoming blogs. Follow this cryptography technology playlist to explore more such demos.
CAN Protocol Hands-on Course with CAN analyzer
Tools needed
Now to achieve this, we will be needing some Hardware and Software tools.
In Hardware part, we will be needing:
1) ElecronicsV3 Development Board: Buy Link
2) Double Breadboard:
3) ST7789 Color LCD Screen: LCD screen for printing images
ElecronicsV3 is a development board built on NXP Semiconductors S32K144 Microcontroller. S32K144 MCU is an automotive Microcontroller based on ARM Cortex M4 Processor and is part of NXP S32 Automotive Microcontroller family.
ElecronicsV3 board which is built on S32K144 MCU has a cryptography peripheral present in it, called as CSEc(Cryptography Security Engine). Which is a SHE standard based security sub-system for doing cryptographic operations and establishing secure communication b/w the ECU and the sensors/actuators of the car.
We are gonna use CSEc peripheral of S32K144, to do encryption/decryption of data
ST7789 Color LCD Screen
In software we will be needing
1) S32 Design Studio IDE: Which is a Desktop Application for programming S32 Family of microcontroller’s/microprocessor.
2) LCD image converter: Desktop application to convert the image into string of bytes
S32 Design Studio is the IDE that is used for development of Embedded Software Development on S32 family of Microcontrollers. IDE stands for Integrated Development Environment, which is used for doing software development on microcontrollers. ElecronicsV2 board has S32K144 Microcontroller, which is part of NXP Semiconductor S32 family of MCU. Thus, we will be using S32 Design Studio for doing Handson activity with ElecronicsV2 boards,
S32 Design Studio: is an Integrated Development Environment to write the microcontroller programs for S32 Automotive Microcontrollers. Install the S32 Design Studio software in your PC and in addition to it user also have to download the Real Time Driver (RTD) package for S32K1 MCU. Refer to this blog for full installation guide of S32 Design Studio step-by-step: Getting Started with S32 Design Studio Part 1 | Gettobyte
We will use this software to convert the images into string of bytes. How to use this software is mentioned below:
Getting Started
Okay so now let’s get started with it, i hope so you guys have gathered all the software/hardware that i have mentioned above and connected all the hardware items. We will at first directly gonna do the practical implementation and then going to dwell deep into it.
Now for microcontroller programming on ElecronicsV2, I am making a separate GitHub repo, where all the demo examples and peripherals codes would be committed with time. Clone the repo, into your local PC. Link of the repo:
https://github.com/gettobyte/ElecronicsV2
Now in the repo, navigate to: Peripheral Drivers-> CSEc , here you will see different examples related to cryptography technology in ElecronicsV2 Development board. 
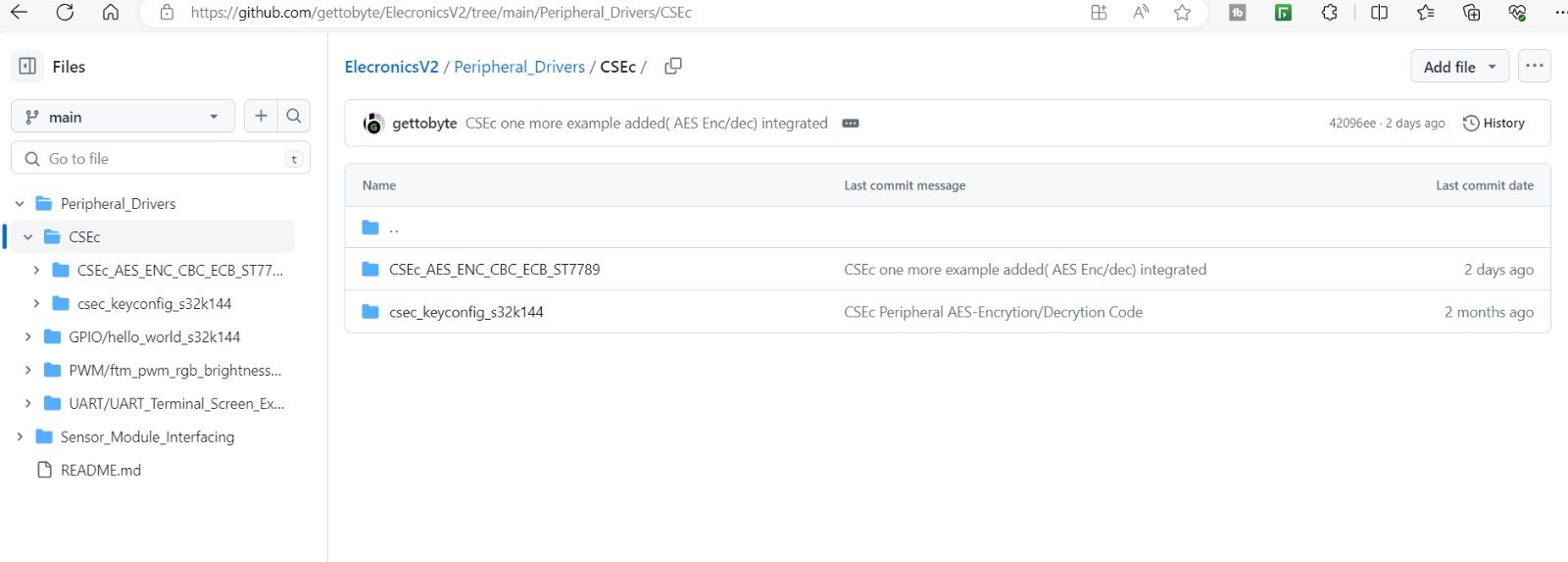
The CSEc_AES_ENC_CBC_ECB_ST7789, is the project for which demo video is shown to you in the starting of the blog. We are going to execute and understand this project.
After cloning the project into your PC, you can see the same folder structure as shown to you at GitHub repo at the path Peripheral_Drivers->CSEc:
Now open the S32 Design Studio and we have to open the Project CSEc_AES_ENC_CBC_ECB_ST7789 into it. CSEc_AES_ENC_CBC_ECB_ST7789 is already developed code, so to open it navigate to file->Open Project from File System To know how to open already developed project in S32 Design Studio, refer to this blog: Getting Started with S32 Design Studio Part 1 | Gettobyte.
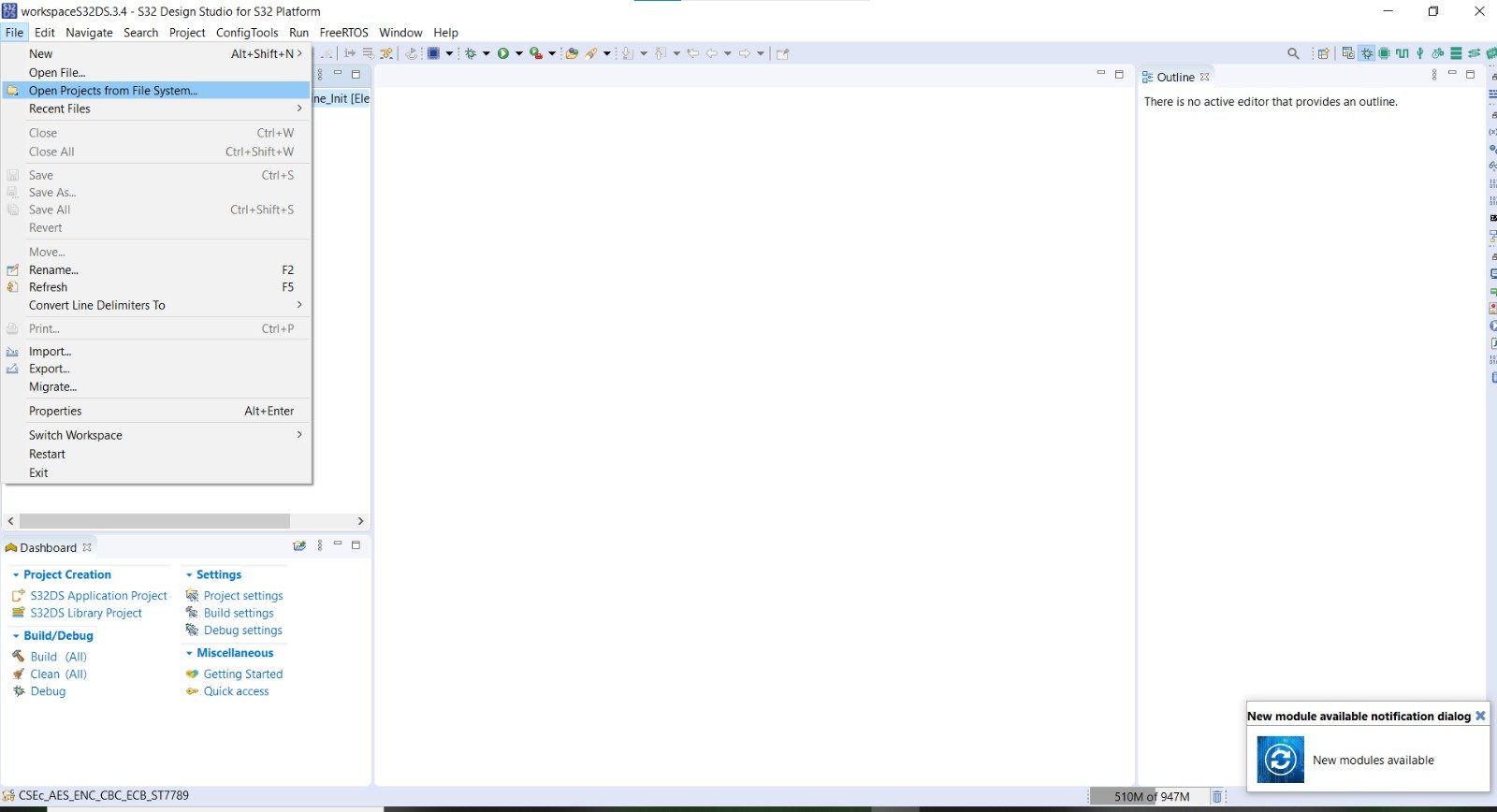
After opening the project, you can see it open in project explorer window of S32 Design Studio.
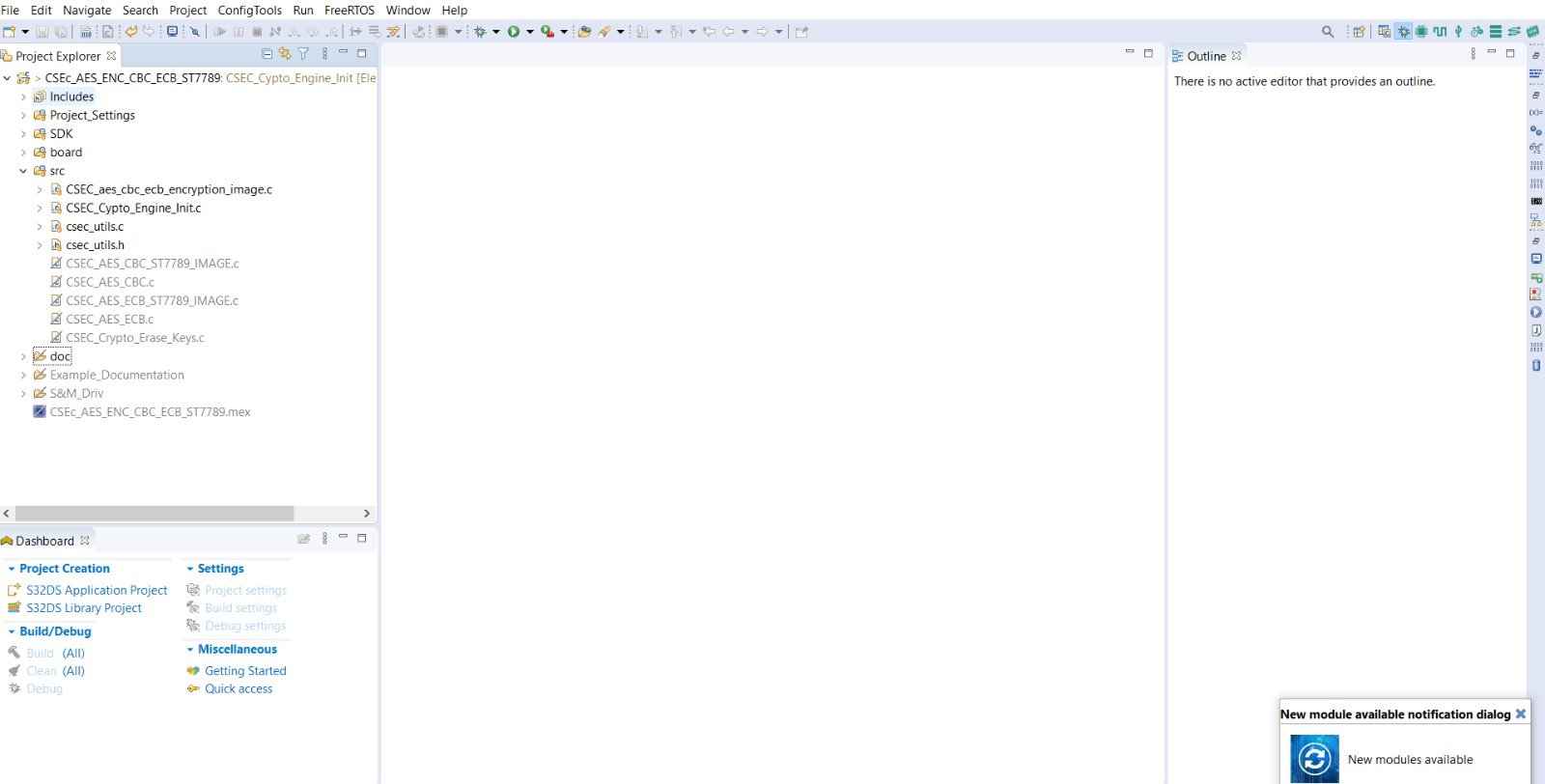
Opening the Cryptography example projects
Opening the Cryptography example projects in S32 Design Studio. In this example project you will find 7 projects:
- 1) CSEC_Crypto_Engine_Init:
- 2) CSEC_Crypto_Erase_Keys:
- 3) CSEC_AES_CBC:
- 4) CSEC_AES_ECB:
- 5) CSEC_AES_CBC_IMAGE_ST7789:
- 6) CSEC_AES_ECB_IMAGE_ST7789
- 7) CSEC_aes_cbc_ecb_encryption_image
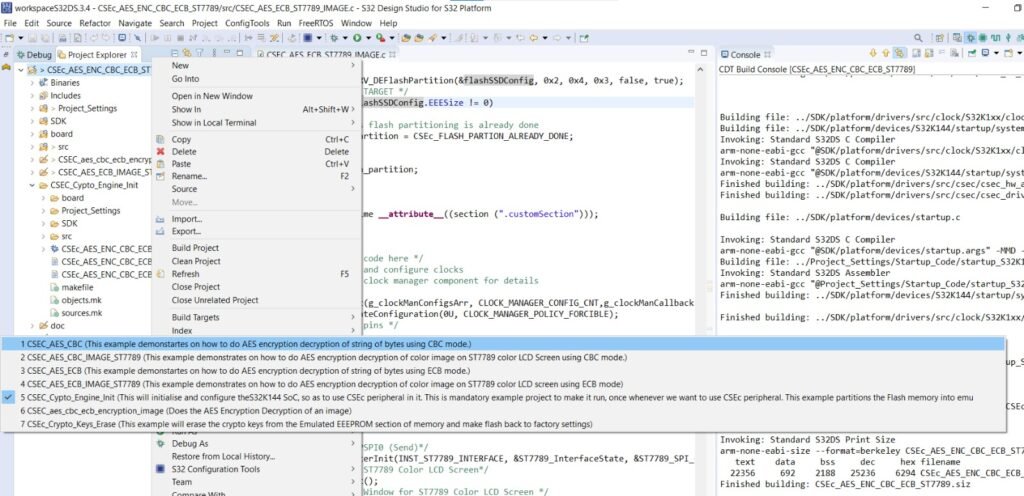
To Open these projects, Right click on project and go to Build Configurations –> Set Archive
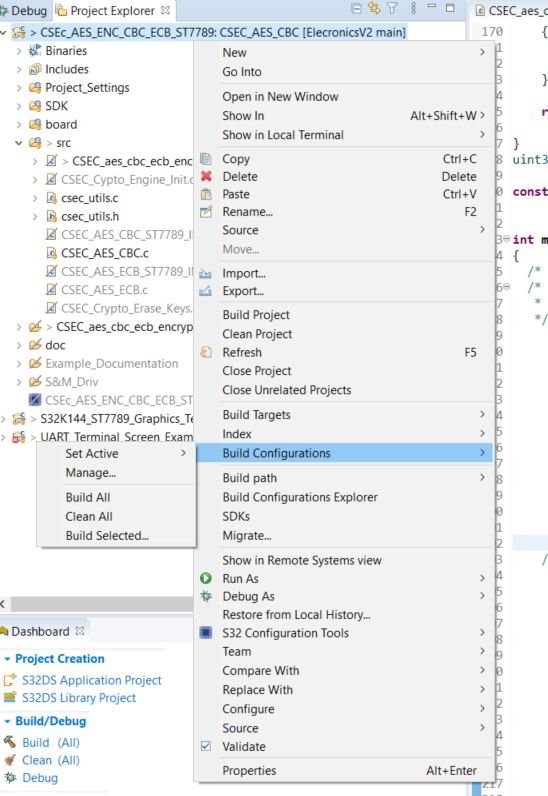
After hovering over the Set-Archive tab, you will see list of all example project:
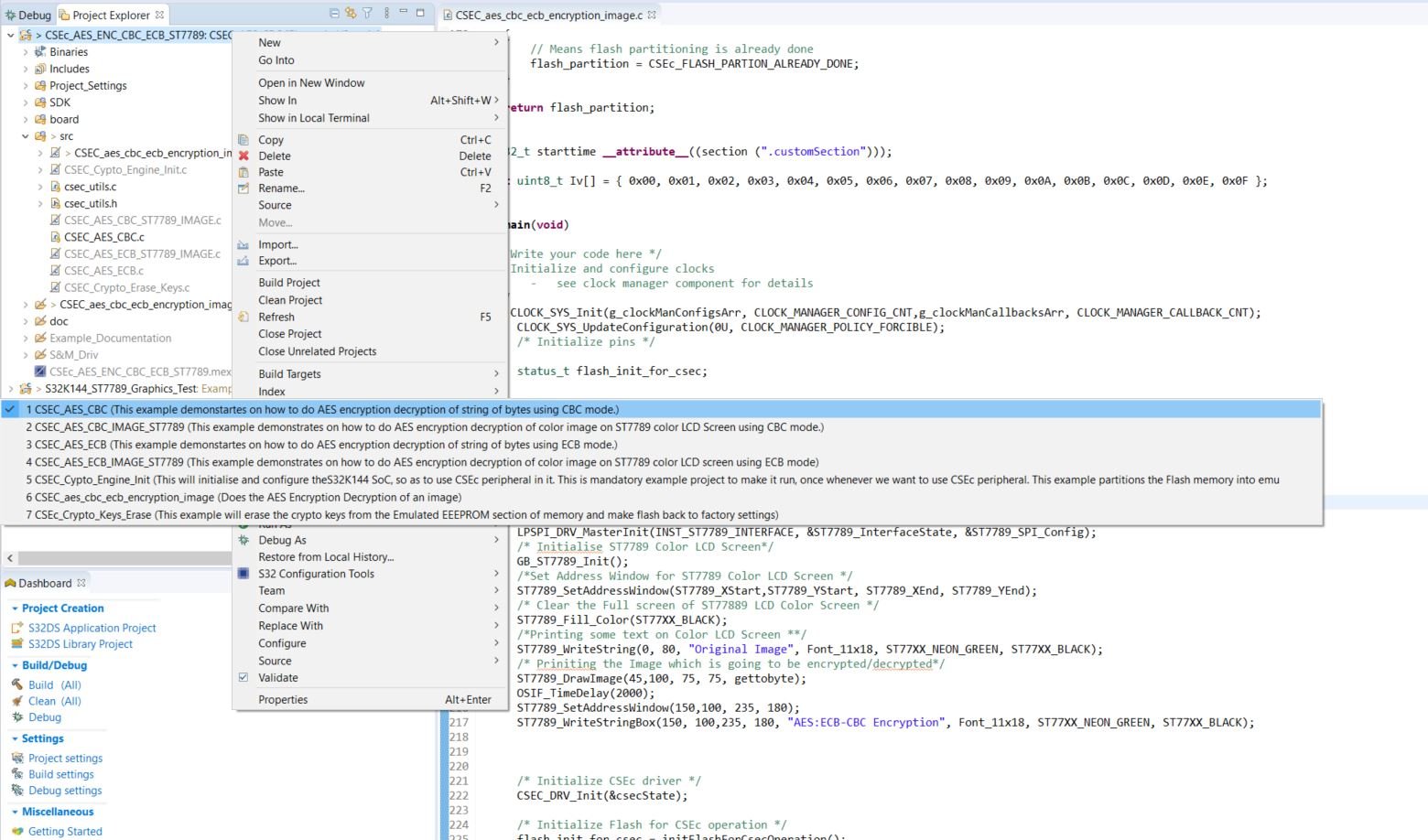
Select the project, which you want to explore, and you will see its name, adjacent to your project name in the project explorer.
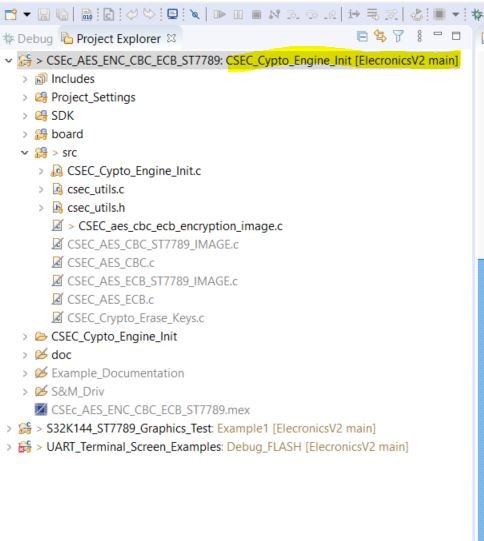
Under the src folder, you will see different .c files. There is one .c file for each of the example projects. By double clicking on the corresponding .c file, you can open that file and explore it
Building the Cryptography projects
Okay so you have opened your project in S32 Design Studio, now it’s time to build the project. For building the project in S32 Design Studio. Simply click on project name and go to menu as shown in below pic:
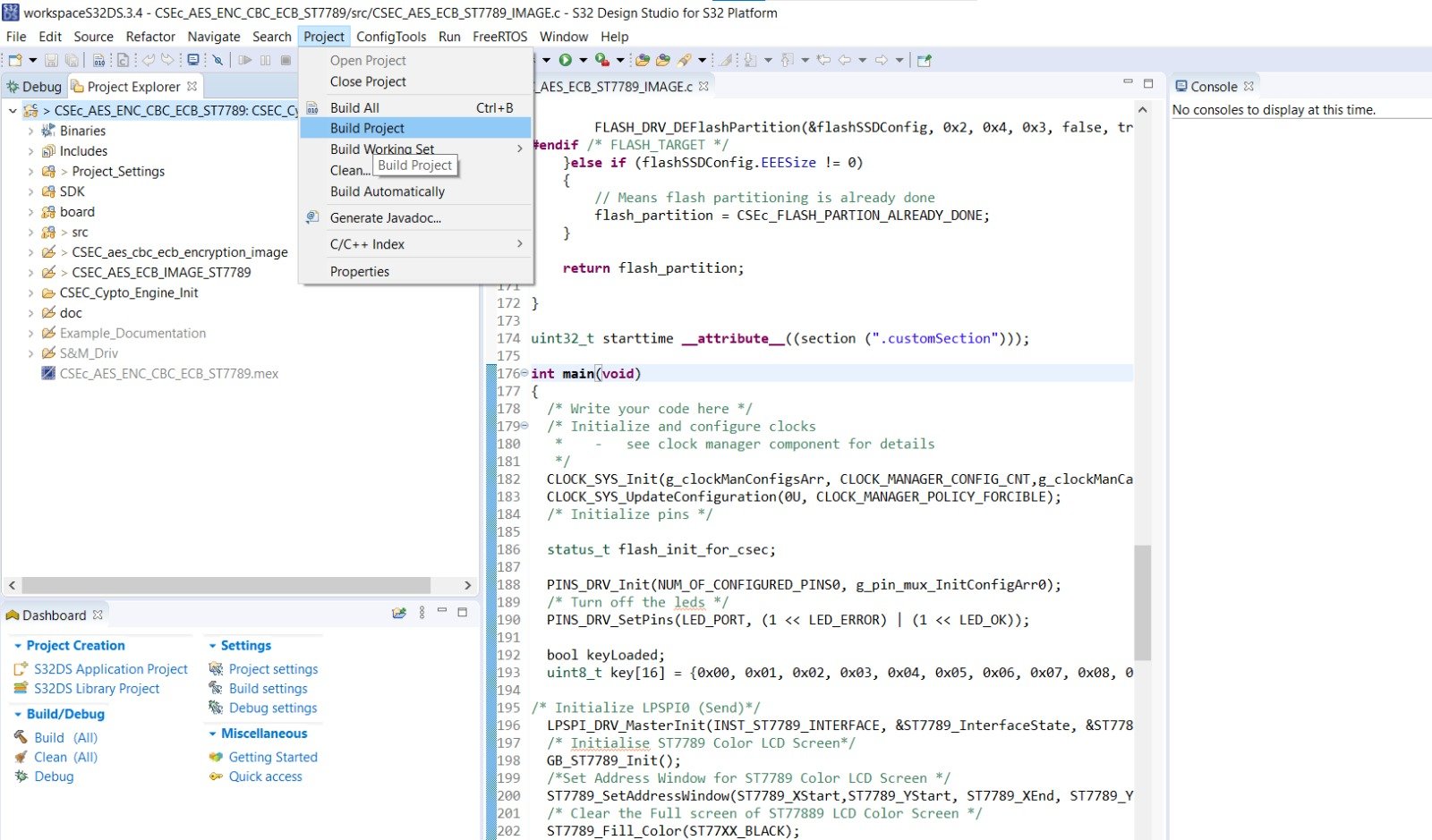
On doing so, you will see a console perspective in which code is compiling.
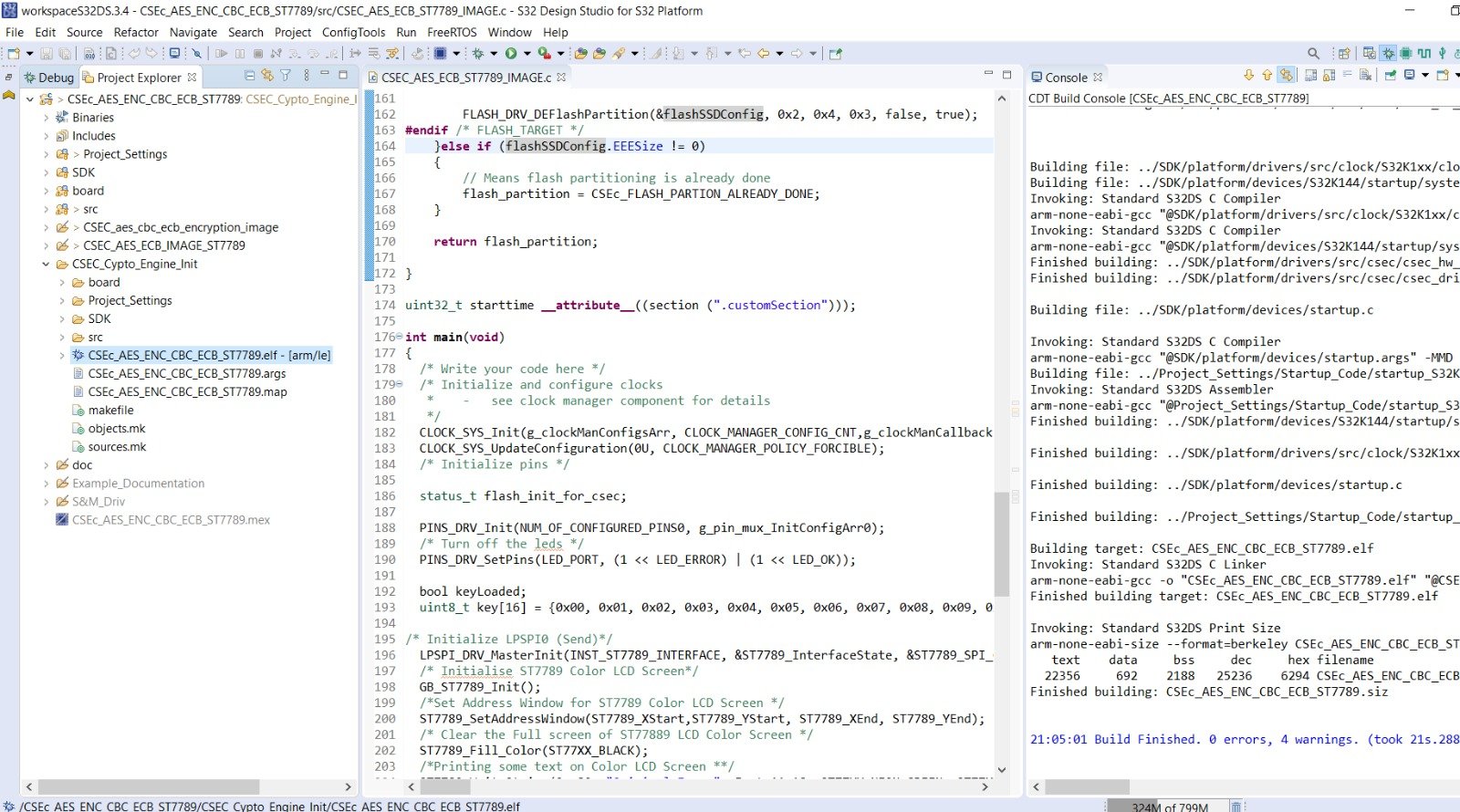
Some pointers to be taken care of:
- 1) Select which example project you want to build, by Right clicking on project name and then selecting which example to use by going to Build Configuration -> Set Archive:
2) After your project is builded, you will see, a corresponding example project name folder in Project explorer, inside which you will find binary files:

Running/Debugging the Cryptography project
Okay so now, we have got the ELF file of our project. Now it’s time to dump this elf file into our project. For doing so, we need a hardware tool called as debugger to transfer this elf file which is in our PC to the microcontroller S32K144 which is in ElecronicsV2 board.
The hardware tool that we are going to use is JlinkV9 debugger which is universal debugger for all ARM Cortex M4 based microcontroller. Viewers can buy this debugger from here: JLink V9 Debugger Emulator – ARM MCU Development Tool – Electronics Infra.
To connect JlinkV9 debugger with ElecronicsV2 board, follow this video or users can refer the Getting to know Hardware Section of Getting Started Manual of ElecronicsV2:
After doing the hardware connection’s, Now we have to do some Hardware Debugger configuration’s in S32 Design Studio IDE so as to detect the debugger hardware tool: JlinkV9 and ElecronicsV2 Board.
For doing so, follow the below steps:
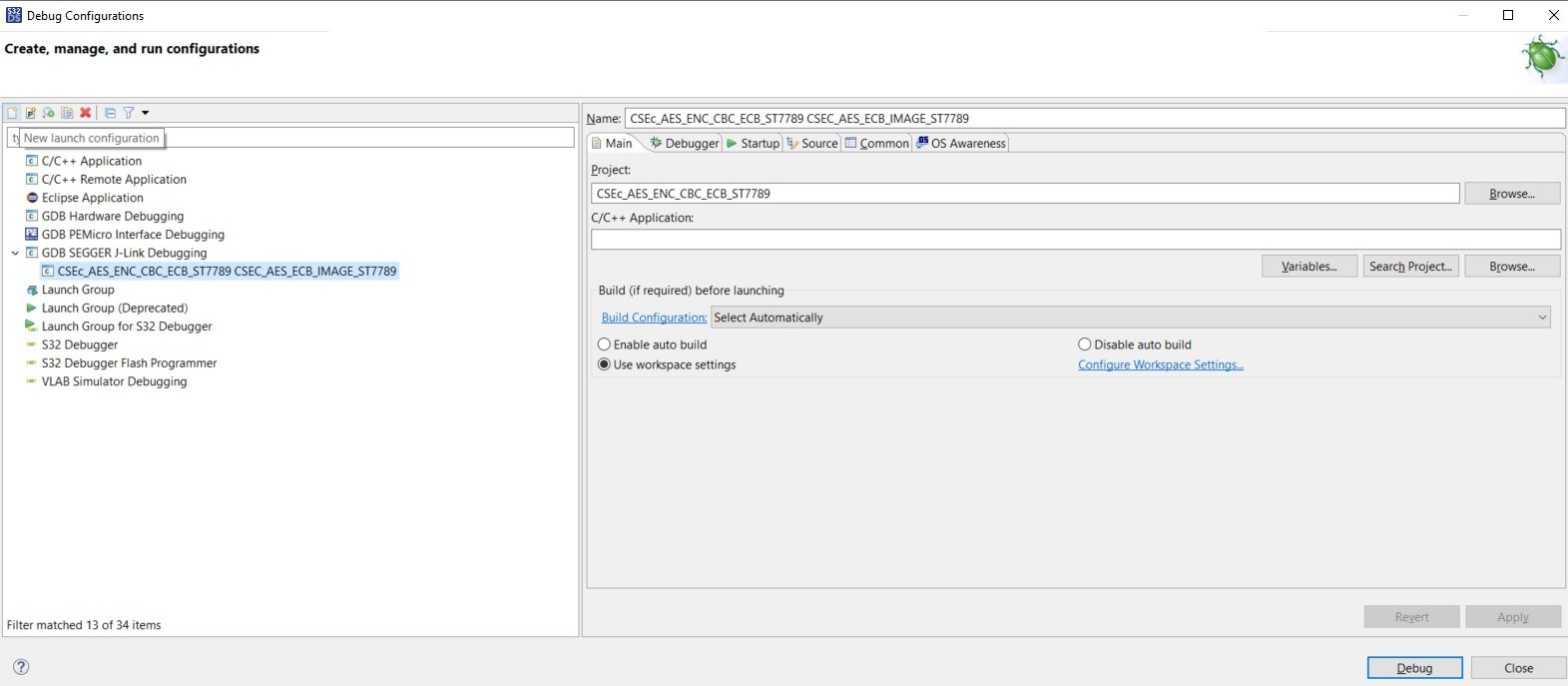
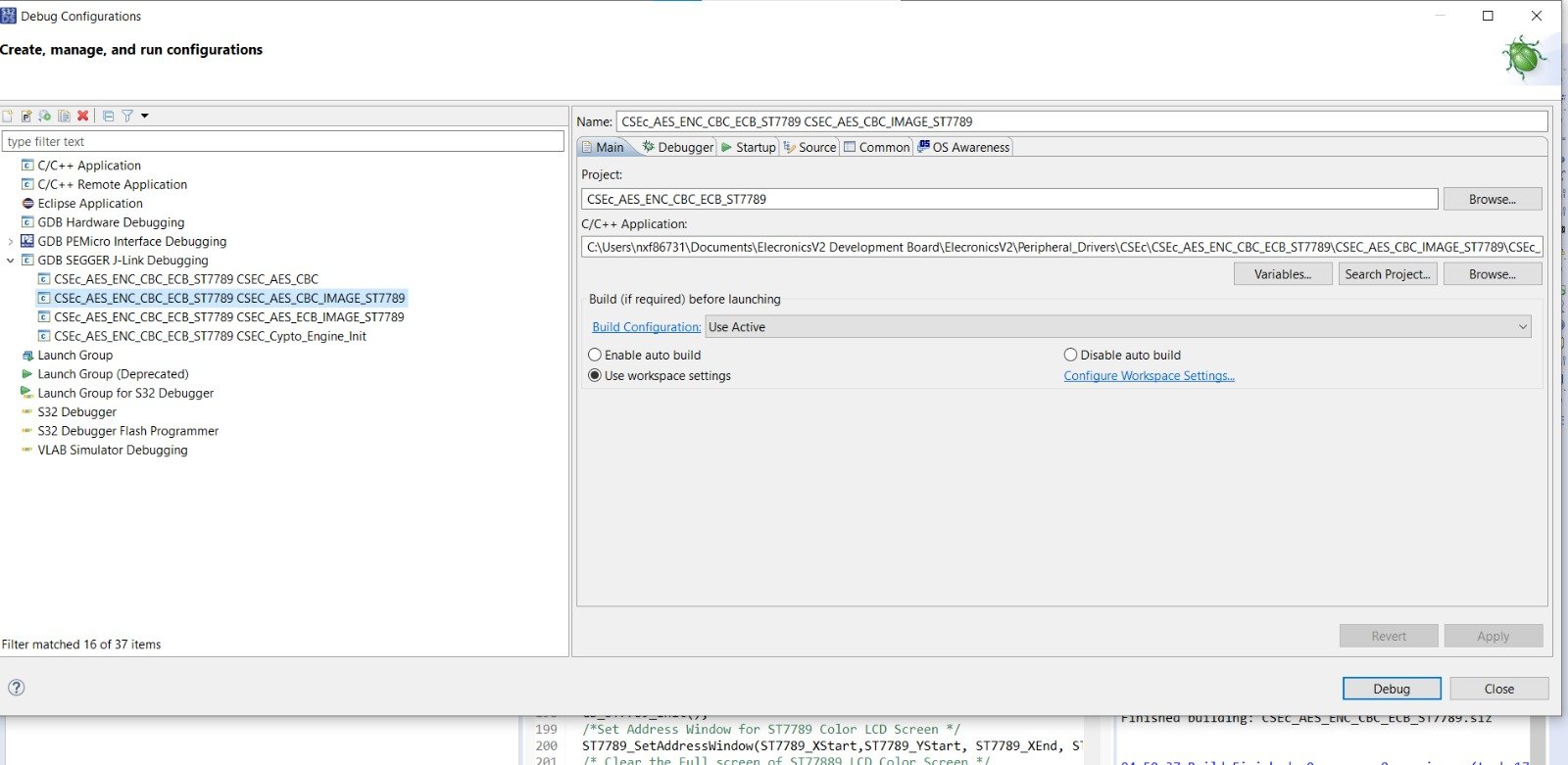
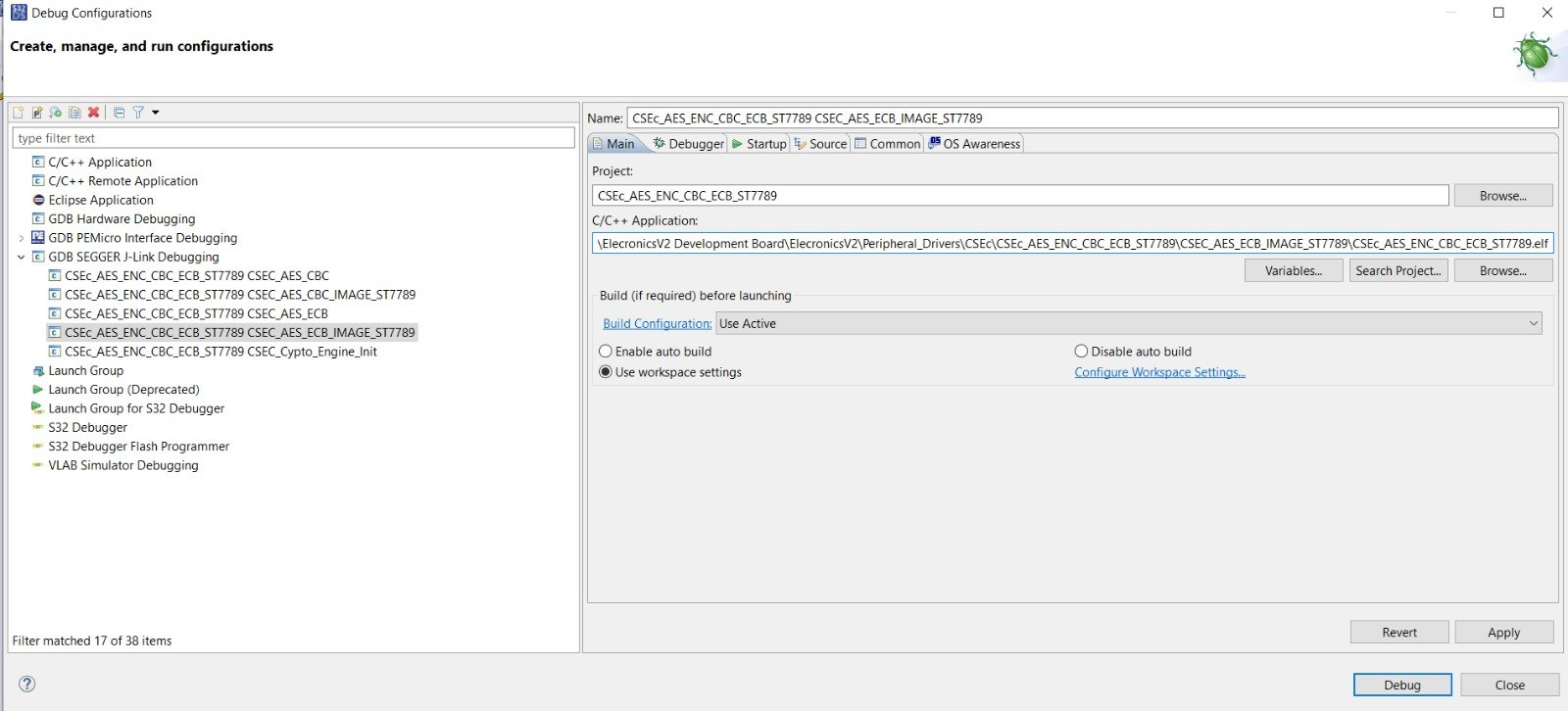
- 1) Open the Debug Configuration Window:

Debug Configuration Menu in S32 Design Studio 2) Now in the Debug Configuration window, you will see list of hardware debuggers that are supported in S32 Design Studio. We will select the GDB SEGGER J-Link Debugging

Debug Configuration window in S32 Design Studio 3) After that click on top left icon of New Configuration, after which you will see a new debug configuration of your project is made:
Making Debug configuration of project 4) After that browse the elf file in C/C++ application tab. And select the Build configuration as Use Active.
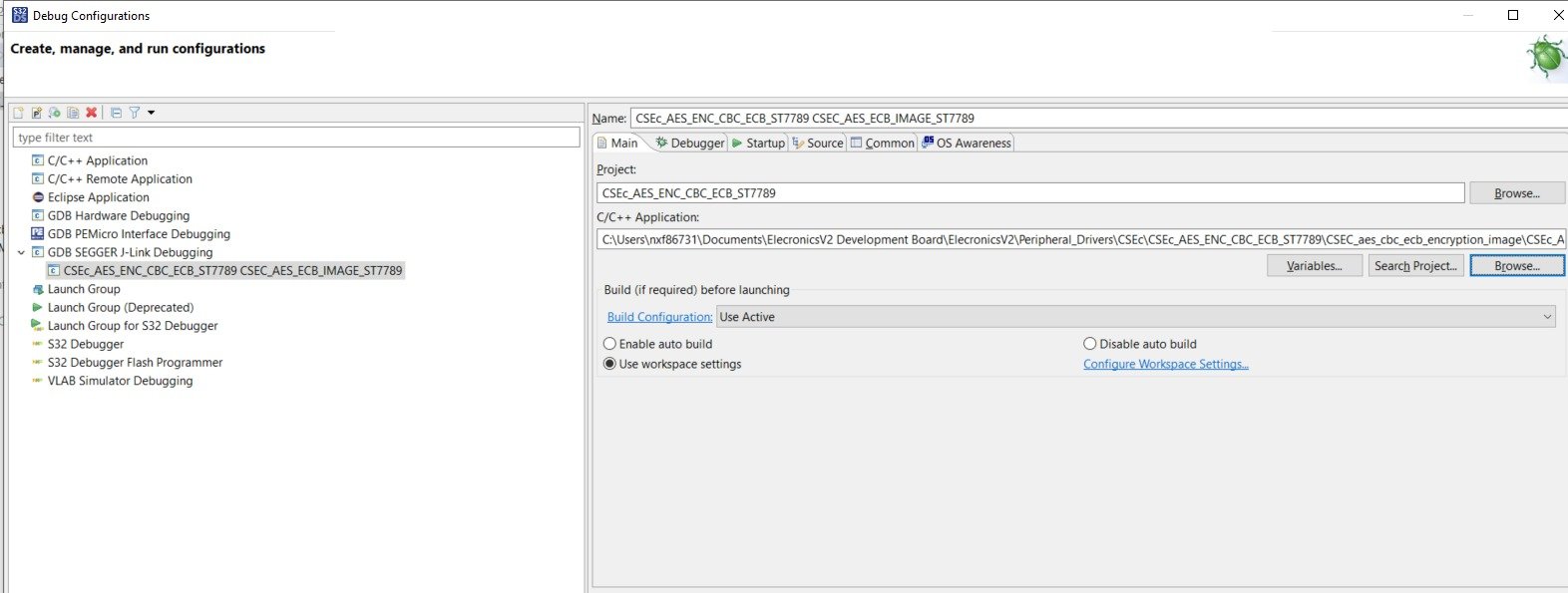
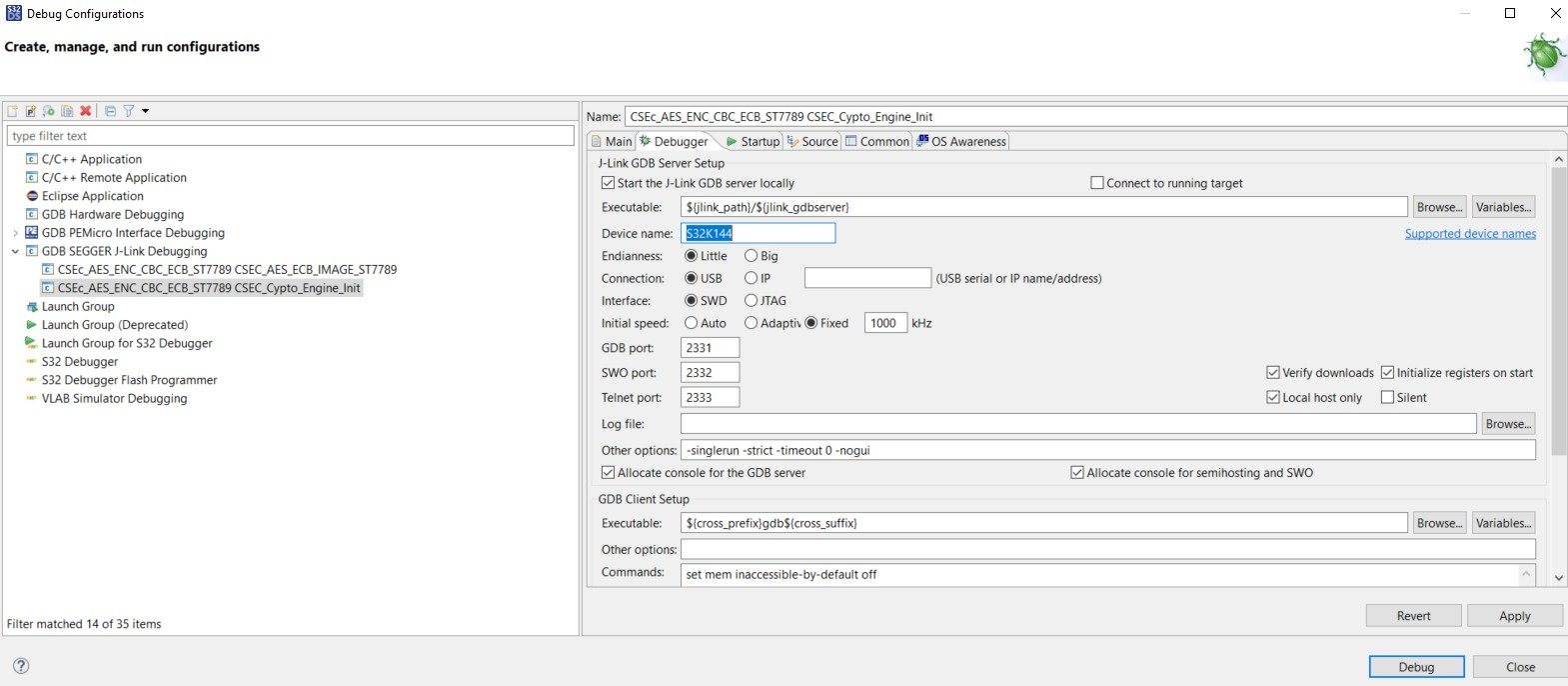
Main tab configuration in Debug Configuration for S32 Design Studio 5) In the Debugger tab of Debug Configuration, you have written the Device Name: S32K144:
These steps will be same for all the example projects. Next steps will only be for CSEC_Crypto_Engine_Init and CSEC_Crypto_Erase_Keys example project.
6) In startup tab of Debug Configuration, check the RAM application option. As we have to run CSEC_Crypto_Engine_Init and CSEC_Crypto_Erase_Keys example project from RAM memory of the controller.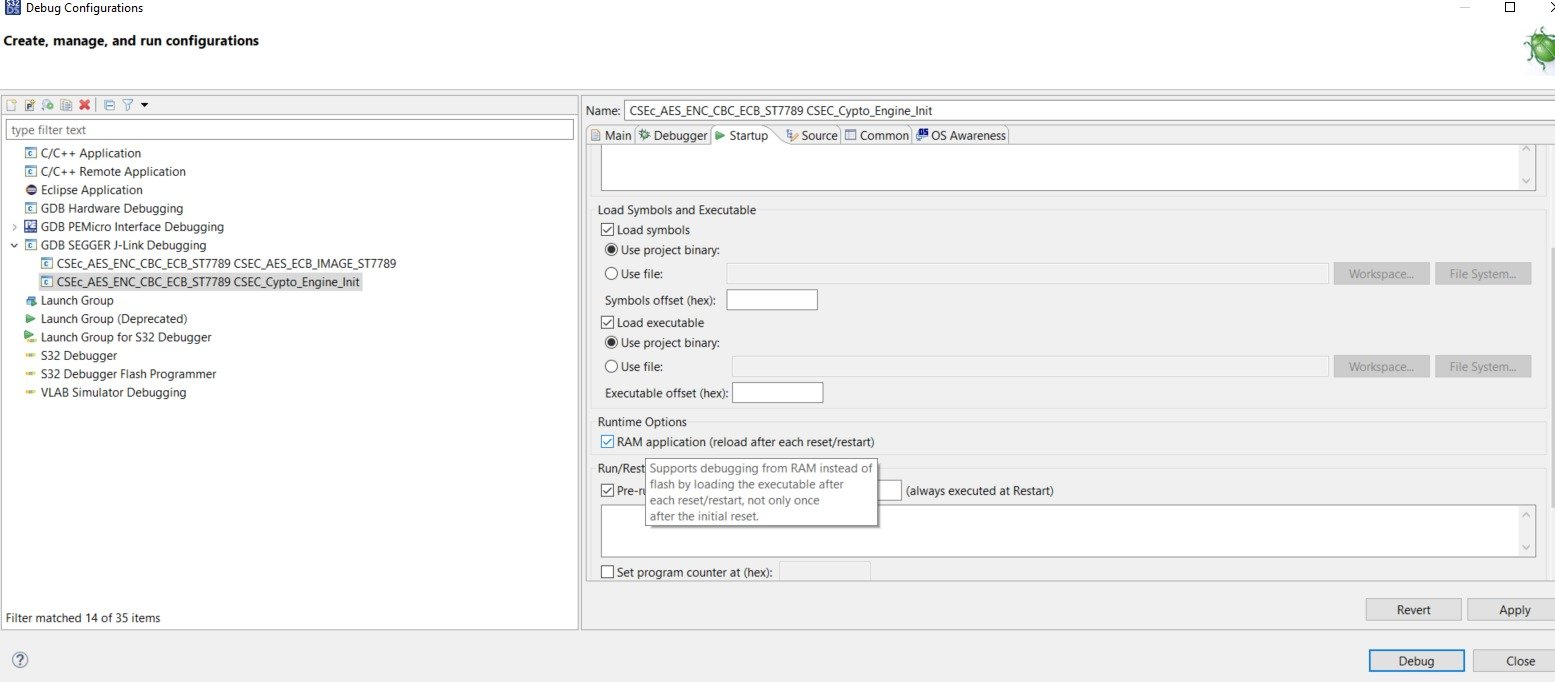
After all these 5-6 steps, click on debug and your debug configuration will be loaded and Debug Perspective will started coming up. In the end something like this will look like in the end.
If your this window come’s up and shows to you. Your debugger and all
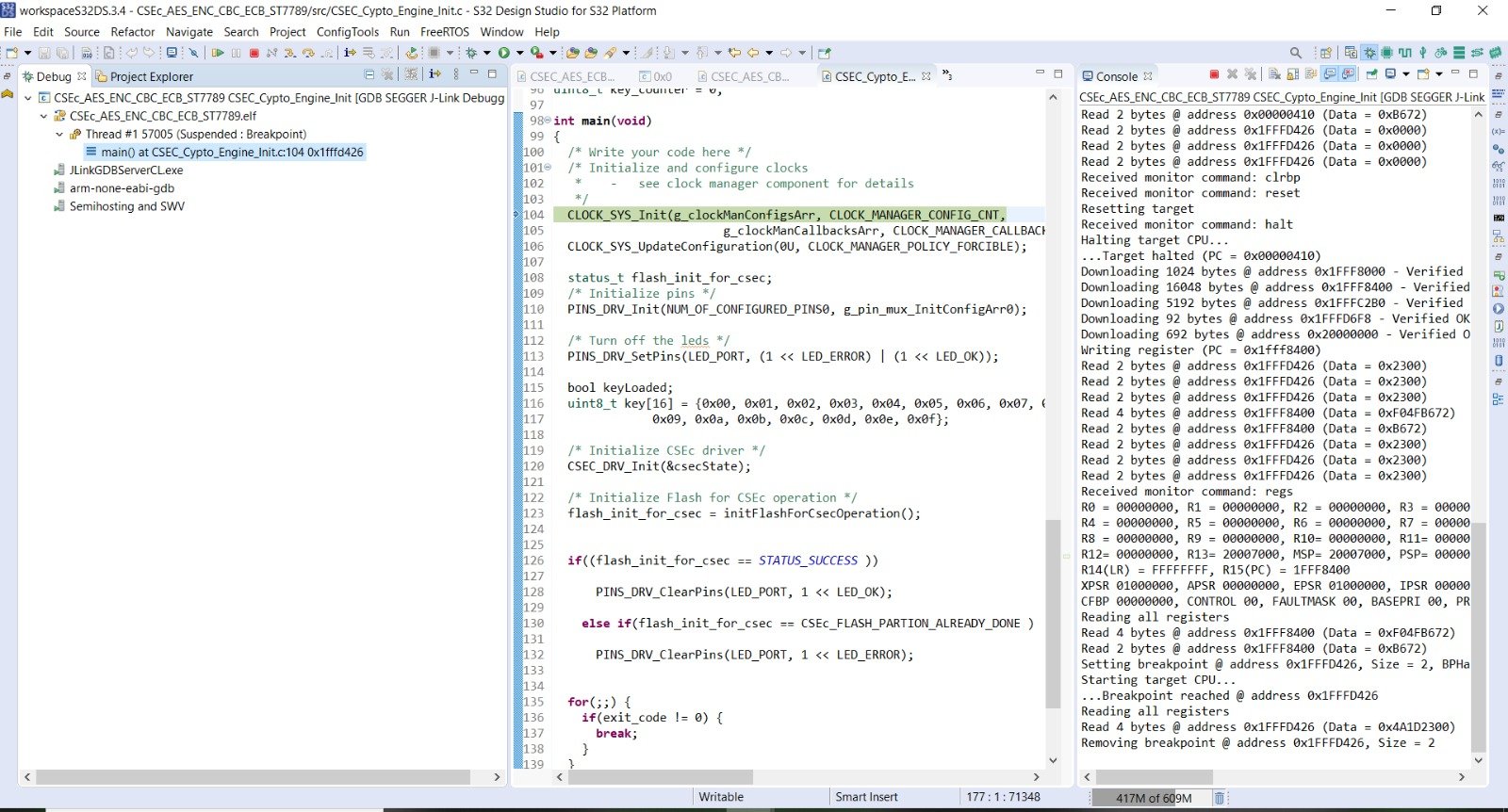
Example Projects on Crytography
This example demonstrates on how to do AES encryption decryption of string of bytes using CBC mode.
Now at first compile the CSEC_Crypto_Engine_Init example project. Refer to building the project section, to know how to build the project.
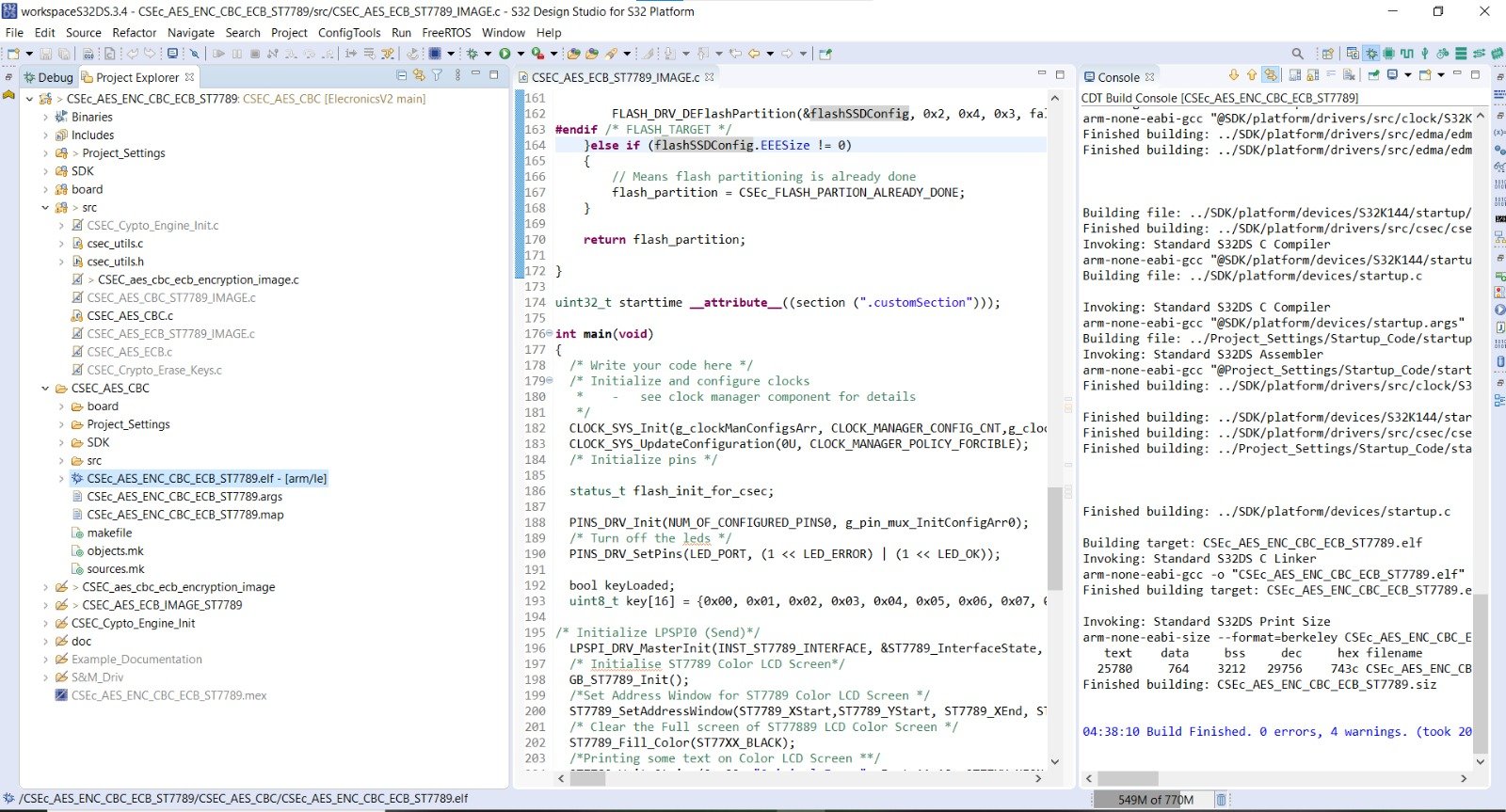
Now after building the example, it’s time to dump the code into ElecronicsV2 and see some action. We will flash the code and debug the code. To do so, do the Debug/Run configuration for this example project in S32 Design Studio as shown below. Refer to Running/Debugging the project session (follow steps from 1-5) to know more in detail.

Expected behavior, after running this example project is that on successfull encryption you will see a green LED turn on
This example demonstrates on how to do AES encryption decryption of color image on ST7789 color LCD Screen using CBC mode.
Now at first compile the CSEC_AES_CBC_IMAGE_ST7789 example project. Refer to building the project section, to know how to build the project.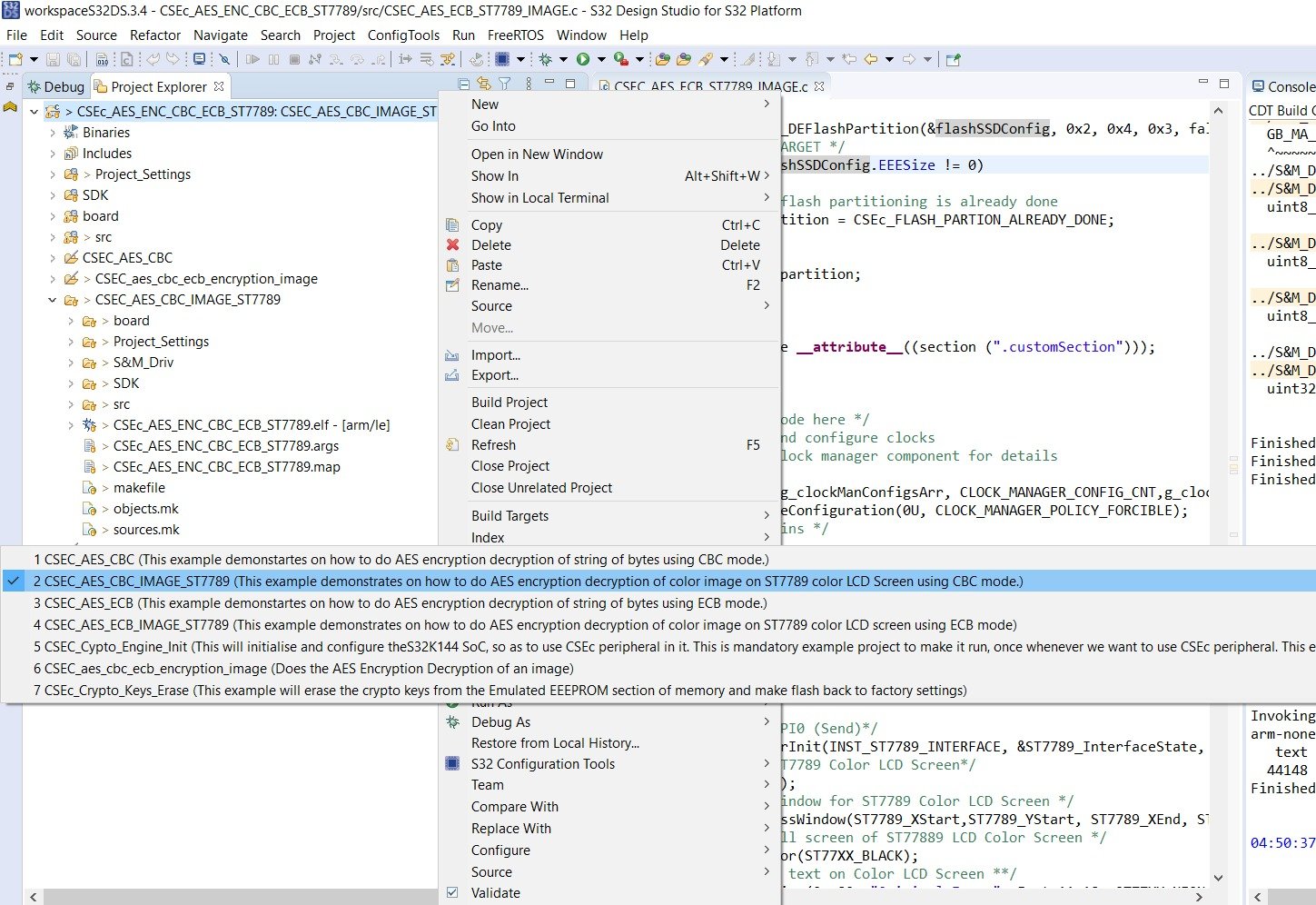
Now after building the example, it’s time to dump the code into ElecronicsV2 and see some action. We will flash the code and debug the code. To do so, do the Debug/Run configuration for this example project in S32 Design Studio as shown below. Refer to Running/Debugging the project session (follow steps from 1-5) to know more in detail.
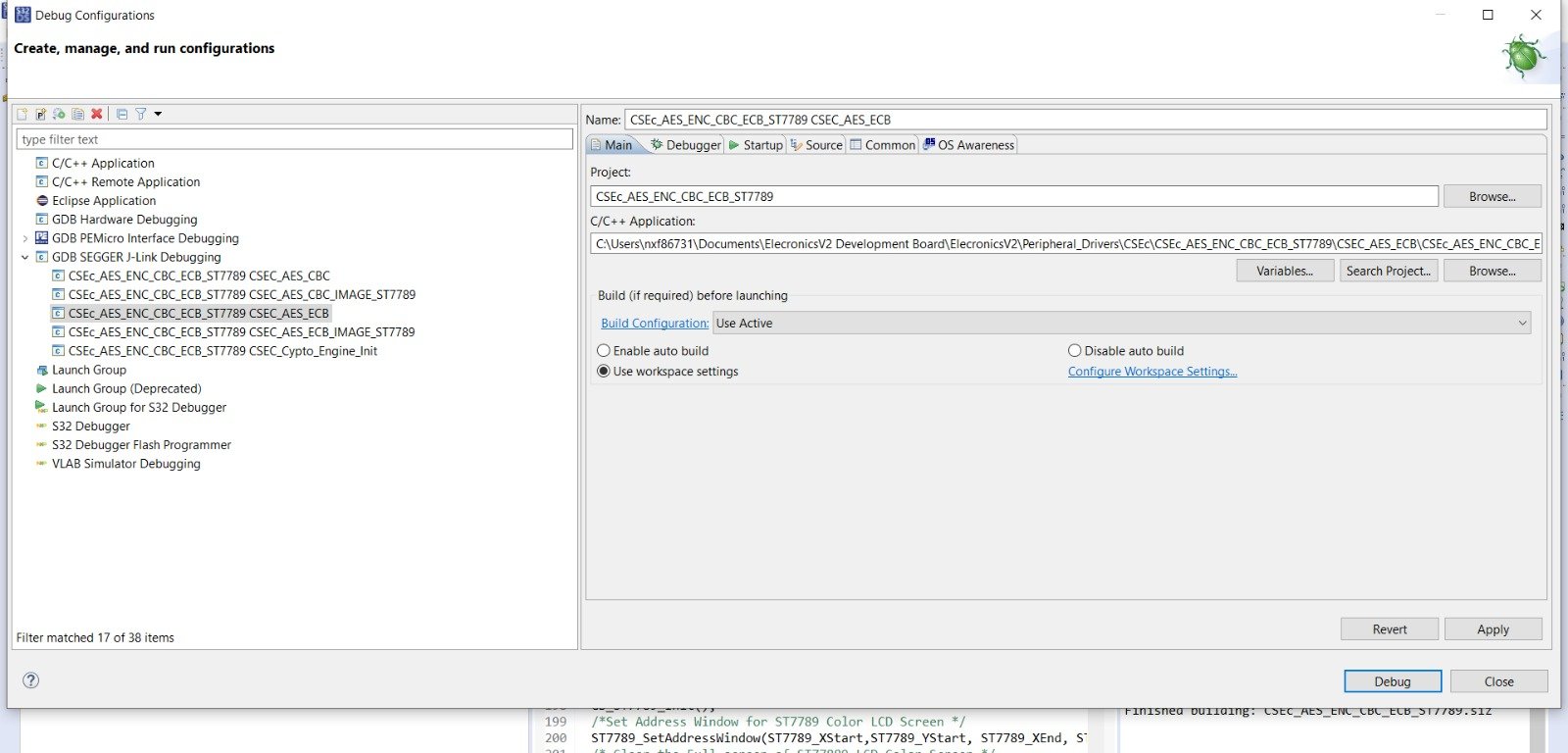
This example demonstrates on how to do AES encryption decryption of string of bytes using ECB mode.
Now at first compile the CSEC_AES_ECB example project. Refer to building the project section, to know how to build the project.

Now after building the example, it’s time to dump the code into ElecronicsV2 and see some action. We will flash the code and debug the code. To do so, do the Debug/Run configuration for this example project in S32 Design Studio as shown below. Refer to Running/Debugging the project session (follow steps from 1-5) to know more in detail.
This example demonstrates on how to do AES encryption decryption of color image on ST7789 color LCD screen using ECB mode of AES crypto cipher.
After running the 1st example project, you can run any example project from 2-6. All will work.
Now at first compile the CSEC_AES_ECB_IMAGE_ST7789 project. Refer to building the project section, to know how to build the project.
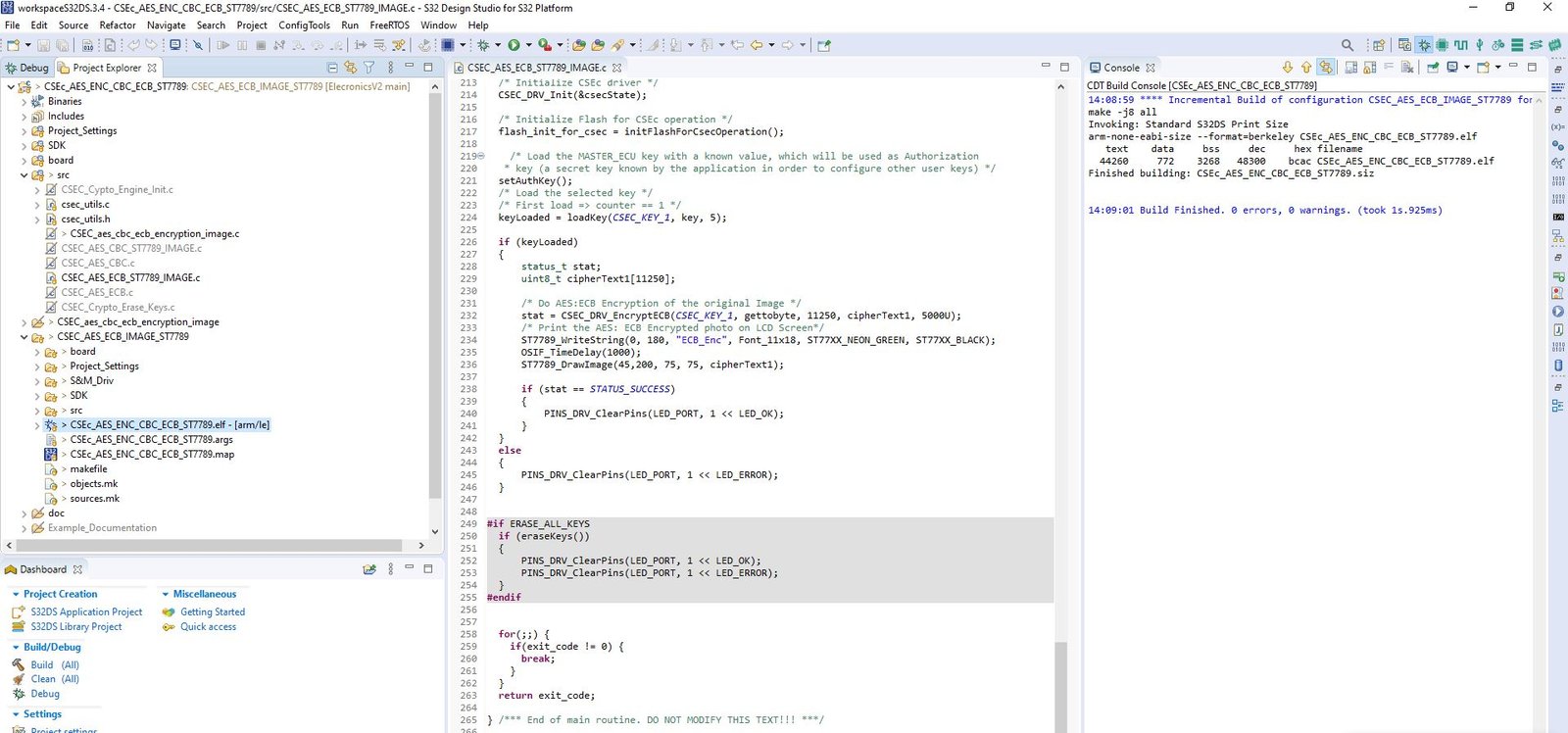
Now after building the example, it’s time to dump the code into ElecronicsV2 and see some action. We will flash the code and debug the code. To do so, do the Debug/Run configuration for this example project in S32 Design Studio as shown below. Refer to Running/Debugging the project session to know more in detail.
This will initialize and configure the S32K144 SoC, so as to use CSEc peripheral in it. This is mandatory example project to make it run, whenever we want to use CSEc peripheral.
This example partitions the Flash memory into emulated EEPROM. This is one time thing which need to be done so as to use CSEc peripheral.
Now at first compile the CSEC_Crypto_Engine_Init example project. Refer to building the project section, to know how to build the project.
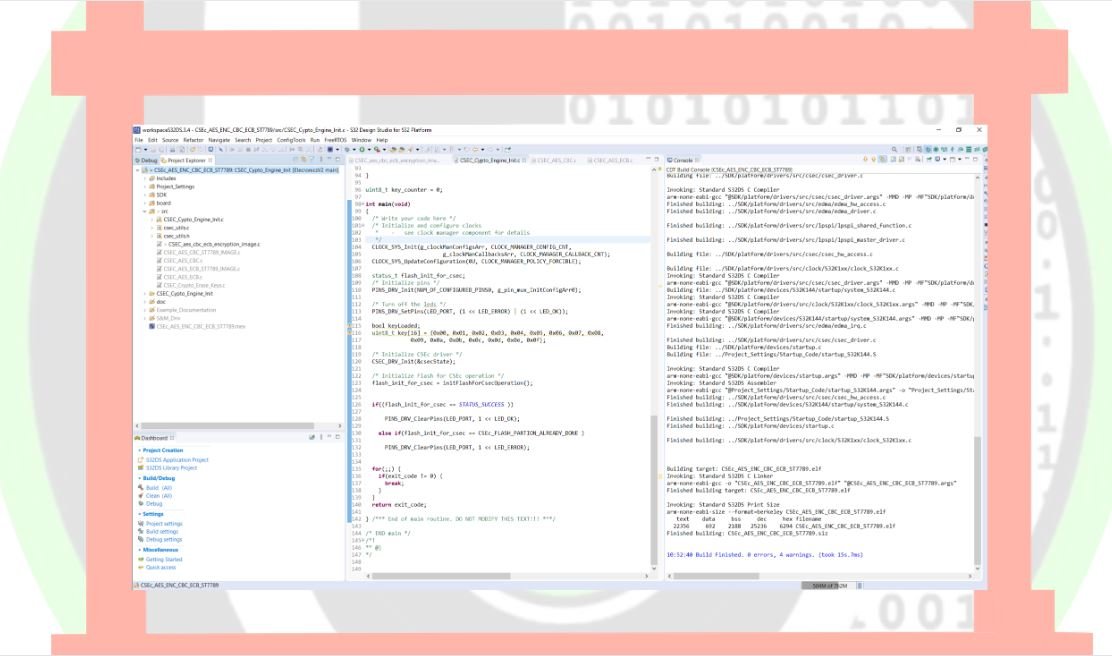
Now after building the example, it’s time to dump the code into ElecronicsV2 and see some action. We will flash the code and debug the code. To do so, do the Debug/Run configuration for this example project in S32 Design Studio as shown below. Refer to Running/Debugging the project session(follow steps from 1-6) to know more in detail.
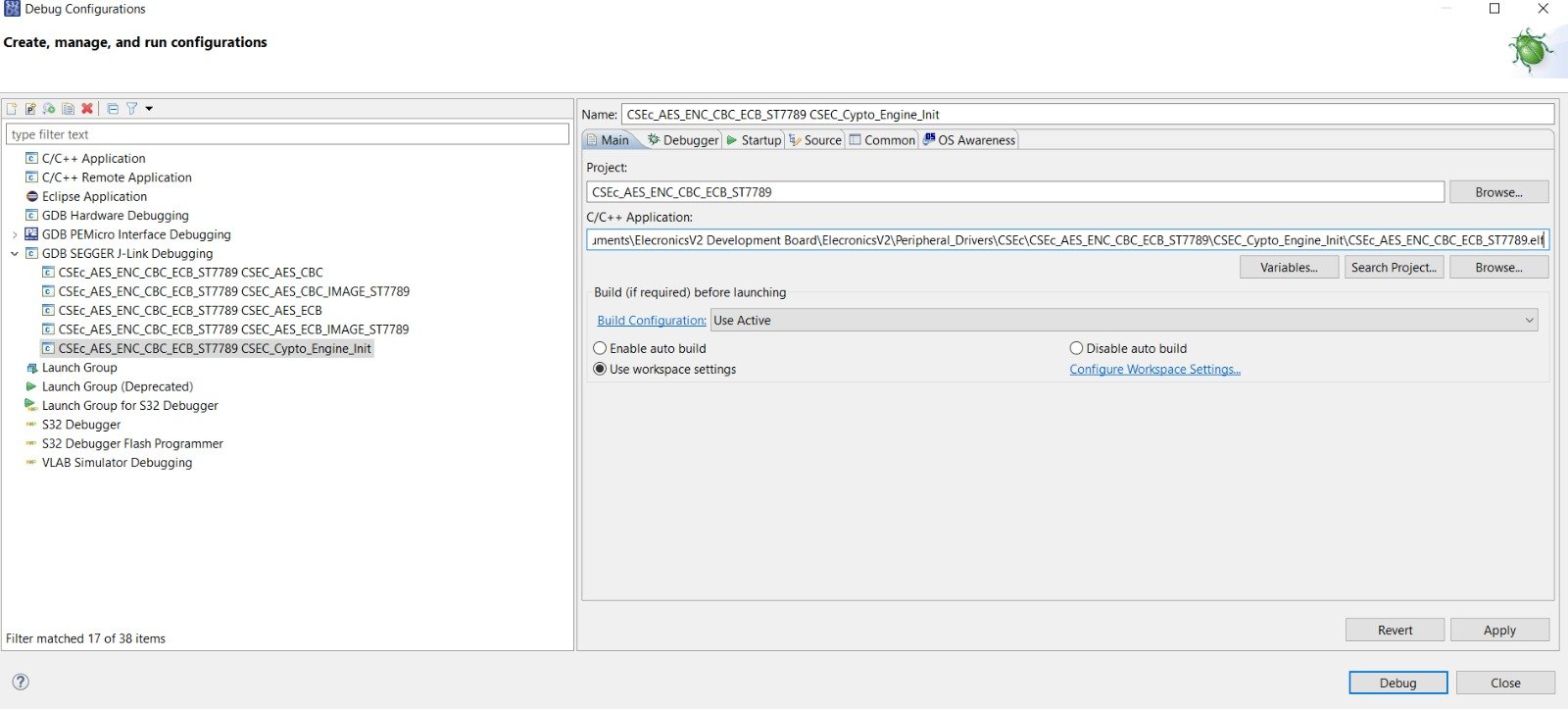
This example initializes the CSEc peripheral. And there are, 2 expected output possible after running this example:
A) CSEc initialization successful –> Green LED lights up
B) CSEc initialization is already done –> RED LED lights up.
After running this example project, flash memory partitioning to emulated EEPROM would be done, which is very first thing that has to be done to use CSEc peripheral. This is the mandatory example project to run that has to be run on the board.
The first time when running the example on the board, or after a key erase, this example should be run in order to enable CSEc operation.
This example demonstrates on how to do AES encryption decryption of color image on ST7789 color LCD screen using ECB mode of AES crypto cipher.
Now at first compile the CSEC_aes_cbc_ecb_encryption_image example project. Refer to building the project section, to know how to build the project.
Now after building the example, it’s time to dump the code into ElecronicsV2 and see some action. We will flash the code and debug the code. To do so, do the Debug/Run configuration for this example project in S32 Design Studio as shown below. Refer to Running/Debugging the project session to know more in detail.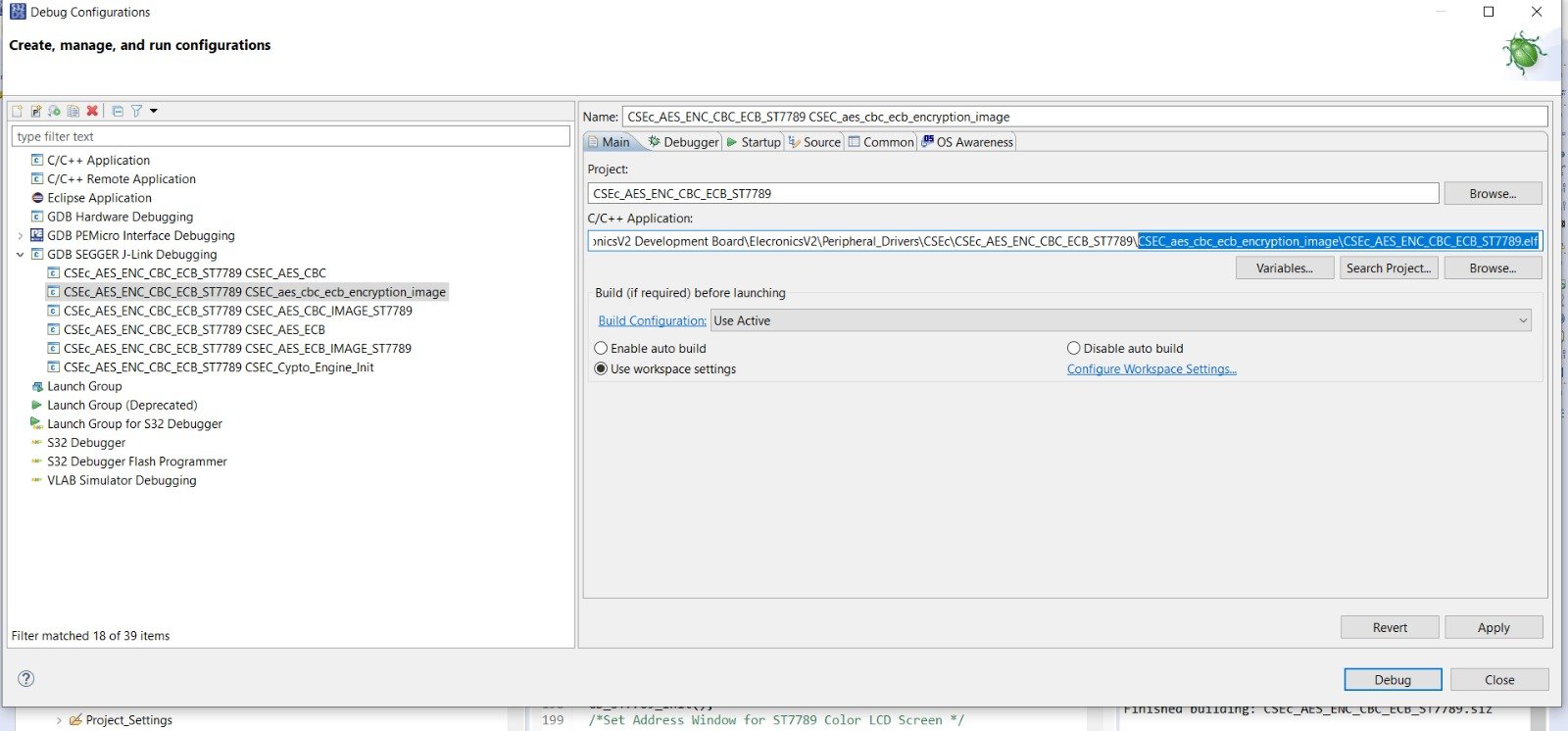
This is the example project, for which video is shown to you initially in the starting of the blog.
To see the text and image printing on ST7789 LCD Screen, make sure that connections to the LCD screen are done properly. Follow this manual, to make the Connections of ST7789 Color LCD screen with ElecronicsV2 Board.
Now Output after running this example project would be:
1) Encryption of image fails: RED LED lights up and on screen only this much is shown:
2) Encryption of image is successfully done: Green LED lights up and on screen both encrypted images are shown.
This example will erase the crypto keys from the Emulated EEEPROM section of memory and make flash back to factory settings.
Important Points to Remember
Example project 2nd is the one which is the DIY project statement which I have stated above.
- 1) Make sure you run the 1st example: CSEC_Crypto_Engine_Init example project, if you are using CSEc peripheral as first time or you have erased the keys. As running CSEC_Crypto_Engine_Init is mandatory to initialize the CSEc peripheral.
- 2) Once CSEc peripheral is initialized, you can run any examples from 2-6 according to your choice. But make sure to increment the counter value of the key in this API, in respective example .c file.
/* Load the selected key */
/* First load => counter == 1 */
/* increment the 3rd parameter of the function: loadKey().*/
keyLoaded = loadKey(CSEC_KEY_1, key, 1);
3) Use the 7th example: CSEC_Crypto_Erase_keys, only when you want to erase the Cryptography keys and de-initialize the CSEC peripheral. And after running this example project, if you want to use CSEc peripheral again its mandatory to run the first example CSEC_Crypto_Engine_Init again.
If you dont run the first example project, all of your Cryptographic operations will fail.
Conclusion
So, this is a simple DIY project that we have done and i hope you guys got the practical experience of doing cryptography using microcontrollers. Now in the upcoming blogs we will dwell into depth of above DIY project implementation. We will understand what is CSEc peripheral? how does it work? Understanding of API’s which are used in above code’s? What is SHE standard? What is the concept of keys and crypto ciphers in SHE standard?
Follow the below cryptography related blogs to grow your knowledge and skill sets in cryptography field.
We will be using the code’s which are used in this DIY blog on cryptography as a reference to corelate theoretical concepts of upcoming blogs to practical understanding
Next Blogs to read
Author
Kunal Gupta


